Over the last few years, the demand for seamless connectivity has grown exponentially in the automotive sector. With the rise of connected cars and the integration of various IoT devices, the automotive sector faces the challenge of managing and monetizing connectivity effectively. This is where connectivity management platforms (CMPs) play a crucial role, and among the key components that contribute to their success, split billing stands out as a pivotal feature.
What is a Connectivity Management Platform (CMP)?
Before delving into split billing, let’s understand what CMPs are and how they have evolved. CMPs are centralized systems that facilitate the management, control and monetization of data connectivity services in connected vehicles. These platforms empower automotive manufacturers and service providers to offer innovative connected services to drivers and passengers while efficiently managing data consumption.
As seen in the chart below, CMP is a component of wider IoT platforms that include a Device Management Platform (DMP), Analytics Platform and Applications Enablement Platform (AEP). Together, these platforms power large-scale IoT applications.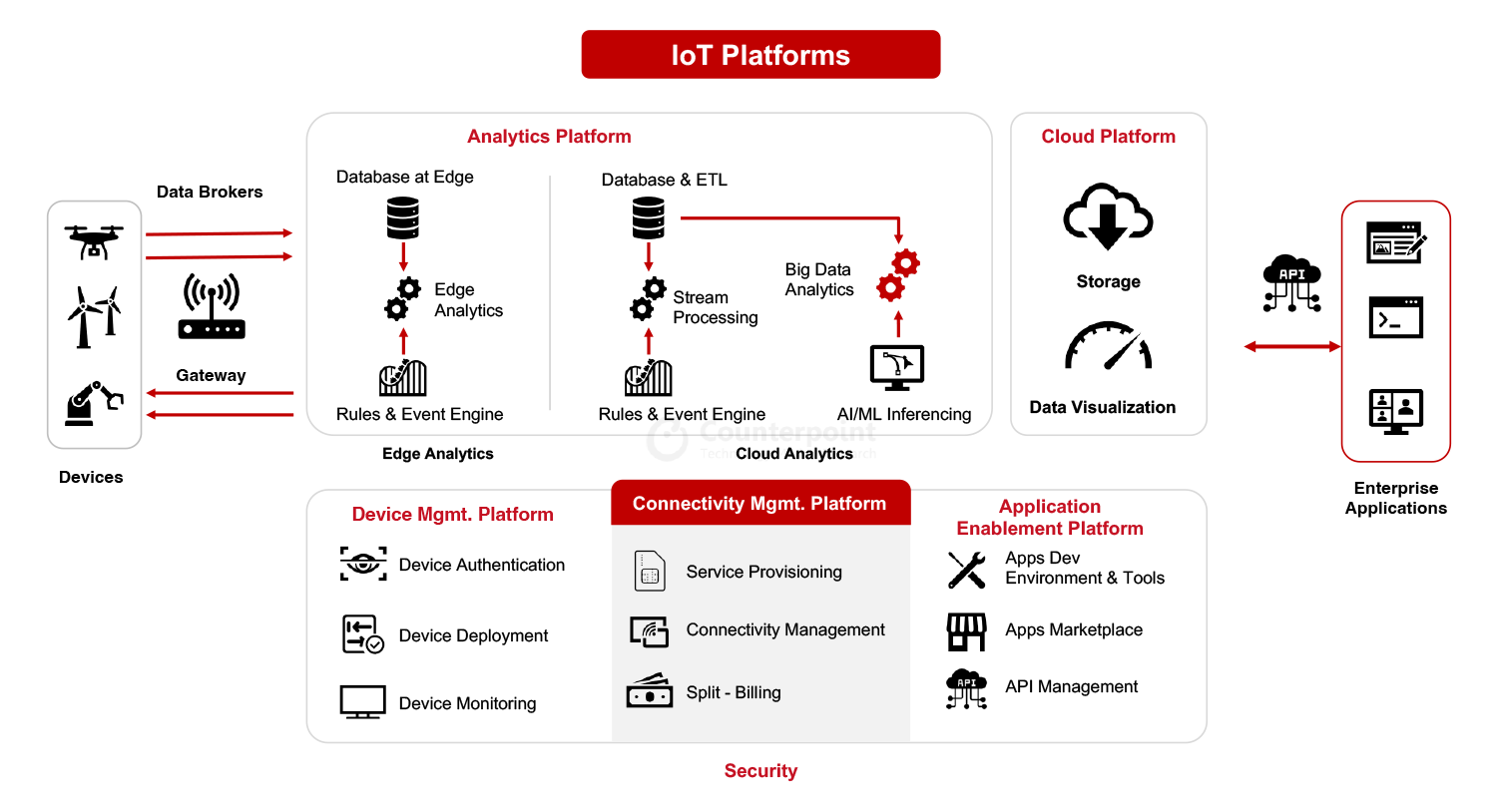
Many connectivity management platforms integrate split billing functionality to cater to the diverse billing requirements of multiple stakeholders in the IoT ecosystem and the automotive industry in particular. Currently, there are many CMPs, such as Cisco, Aeris, Cubic Telecom and Wireless Logic, which have the capability to provide split billing.
Challenges in Connectivity Management for Automotive:
In the past, vehicle connectivity was predominantly limited to basic telematics services and hence the split billing was not so much of a concern. However, the rapid advancement of technology has transformed the automotive landscape. Today, connected cars are equipped with sophisticated infotainment systems, navigation tools, real-time diagnostics, and a multitude of sensors that enhance safety, convenience, and the overall driving experience. In the future, the need for connectivity in cars would be very different with autonomous vehicles and V2X communication.
2022 was a pivotal year for connected cars. According to Counterpoint Research analysis, connected cars surpassed 50% of car sales for the first time with the US, Europe and China as the key markets.
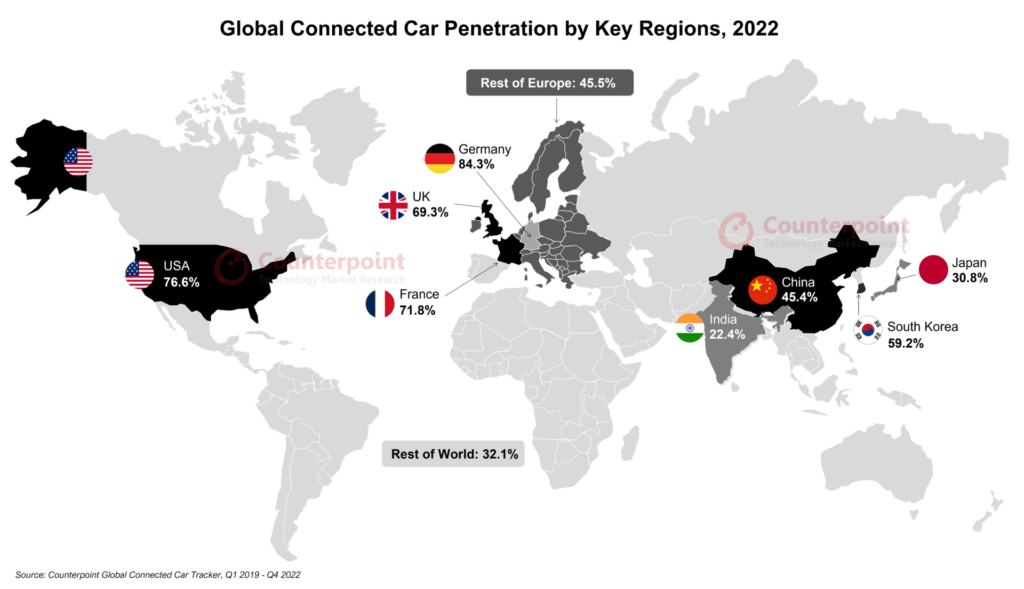
As vehicles become more connected, the complexity of managing connectivity increases. This gives rise to various difficulties for the automotive, including:
- Data Consumption: Connected vehicles generate a vast amount of data, which can quickly lead to exorbitant costs if not managed efficiently.
- Billing and Monetization: With multiple stakeholders involved, such as vehicle manufacturers, network operators, and content providers, it becomes challenging to accurately bill and monetize data usage.
- Personalized Services: Consumers expect personalized services tailored to their preferences, but delivering such services without incurring excessive data charges can be tricky.
- Data Security and Privacy: As vehicles become data hubs, ensuring robust security and privacy measures becomes paramount.
The Role of Split Billing:
In the context of Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity for automobiles, split billing refers to a billing mechanism that allows for the separation and allocation of data usage costs between different entities involved in the IoT ecosystem. This concept is particularly relevant when multiple parties share the data consumption and connectivity expenses of an IoT-enabled vehicle.
In an automobile scenario, various components may require internet connectivity for different purposes:
- Vehicle Manufacturer: The automobile manufacturer may require connectivity for software updates, diagnostics, and data collection to improve its products and services.
- Car Owner/Driver: The car owner or driver may need connectivity for infotainment, navigation, and other personalized services.
- Third-party Service Providers: External service providers, such as insurance companies or fleet management firms, might offer specific services that rely on the vehicle’s connectivity.
Split billing allows the data usage and associated costs to be divided among these parties based on their usage patterns and requirements. For example:
- The car manufacturer might cover the data costs for vehicle diagnostics and software updates, as it benefits the development and maintenance of its product.
- The car owner would be responsible for the data costs associated with personal usage, such as infotainment and navigation.
- Third-party service providers may bear the expenses related to the specific services they offer through the vehicle’s connectivity.
This approach helps create a fair and transparent billing structure, where each stakeholder pays only for the services they consume, rather than a single entity covering all data costs.
What does split billing mean for CMPs?
For CMPs, split billing refers to a specific functionality or feature that allows the platform to support the allocation and management of data usage costs among multiple parties or stakeholders in the IoT ecosystem. This functionality enables CMPs to handle billing and cost-sharing for IoT connectivity services efficiently. The chart below summaries the key aspects and functionalities related to split billing in CMPs.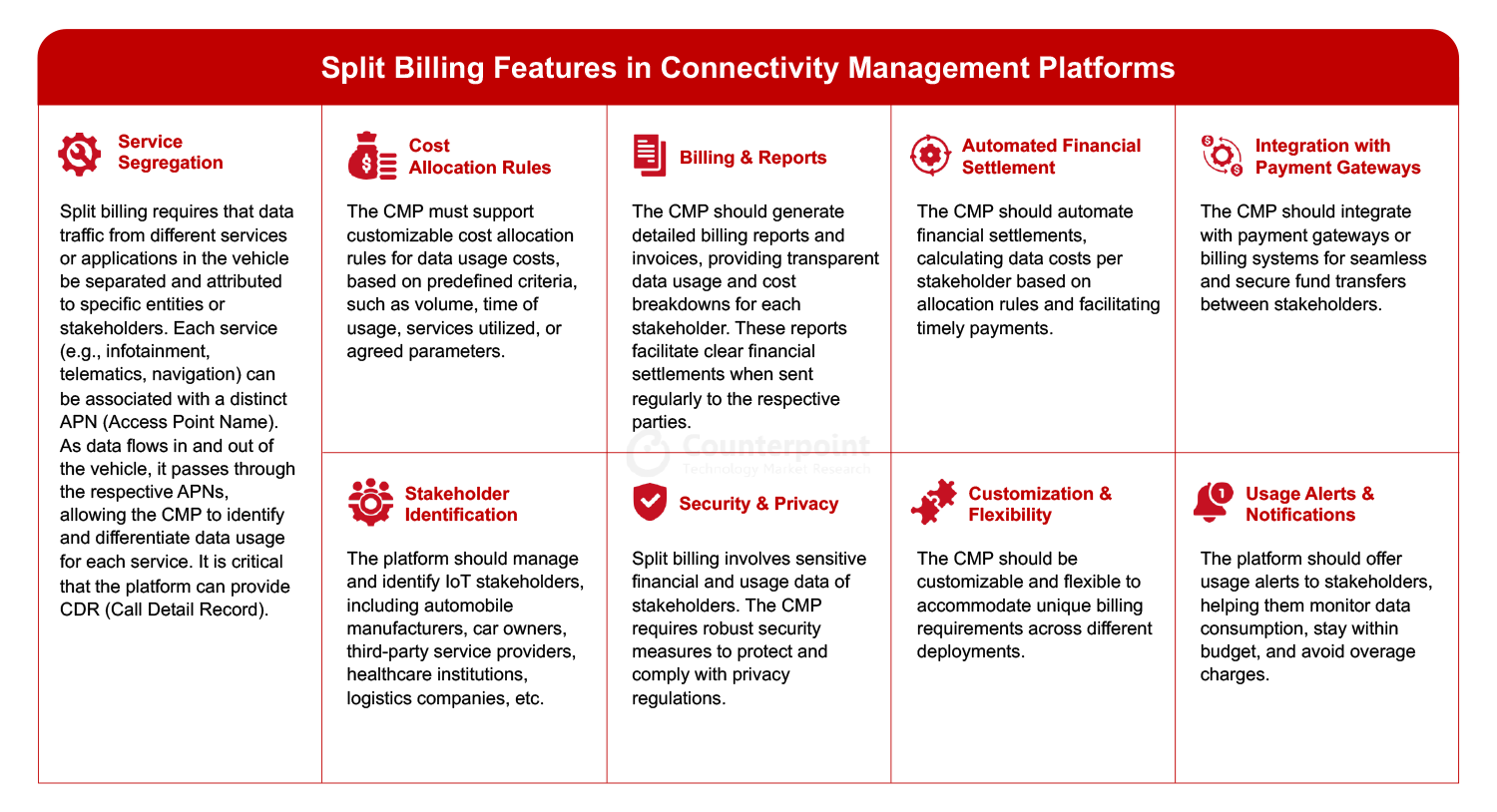 Overall, split billing functionality in a CMP streamlines the financial aspects of IoT deployments, encourages collaboration between different entities, and ensures that each party pays only for the specific services they utilize, making IoT implementations more transparent and cost-effective.
Overall, split billing functionality in a CMP streamlines the financial aspects of IoT deployments, encourages collaboration between different entities, and ensures that each party pays only for the specific services they utilize, making IoT implementations more transparent and cost-effective.
In conclusion, the evolution of CMPs for split billing has been driven by the increasing complexity of connected services, advancements in data analytics and technology, and the growing demands for personalized billing and improved customer experiences. As the IoT landscape continues to evolve, CMPs will play an increasingly vital role in managing data connectivity and enabling fair and accurate billing for the multitude of services offered in the connected world.

